Claim Your Discount Today
Get 10% off on all Statistics Homework at statisticshomeworkhelp.com! This Spring Semester, use code SHHR10OFF to save on assignments like Probability, Regression Analysis, and Hypothesis Testing. Our experts provide accurate solutions with timely delivery to help you excel. Don’t miss out—this limited-time offer won’t last forever. Claim your discount today!
We Accept
- Understanding and Preparing for Statistics Assignments
- Key Statistical Concepts and Guidelines
- Descriptive Statistics: Understanding and Analyzing Data
- Probability Distributions and Scores
- Correlation and Relationships
- Regression Analysis
- Problem-Solving Techniques
- Examples of Statistical Formulas
- Conclusion
Solving comprehensive statistics assignments can feel overwhelming, especially when they cover a wide range of topics like variance, standard deviation, Z-scores, correlation coefficients, and regression equations. However, with proper preparation and a clear understanding of key concepts, completing such assignments becomes manageable and even rewarding. To start, familiarize yourself with the definitions and formulas for crucial terms, as this foundation ensures accuracy in calculations and interpretations. Break the assignment into smaller sections, tackling each component methodically to avoid confusion. Use tools like scatterplots and correlation matrices to visualize data relationships and identify patterns. Whether calculating the interquartile range or applying the least squares regression equation, precision is critical. For those needing extra guidance, seeking statistics homework help is an excellent way to clarify doubts and enhance your approach to problem-solving. Professionals can guide you through complex computations, ensuring your work aligns with academic standards. Additionally, practicing examples involving the addition rule, multiplication rule, and regression analysis will reinforce your understanding and improve your confidence. Remember, solving statistics assignments isn’t just about finding answers—it’s about developing analytical skills that are vital for academic success. By following these guidelines and utilizing resources like statistics homework help when needed, you’ll approach your assignments with clarity, confidence, and a deeper grasp of the subject matter.
Understanding and Preparing for Statistics Assignments

To excel in statistics assignments, it is crucial to first understand the scope of the topics covered. Begin by reviewing the assignment instructions carefully and identifying key concepts like range, variance, and standard deviation. Preparing for an assignment means breaking it into manageable parts, allowing you to tackle each section methodically. Organize your notes, focus on definitions and formulas, and apply them to sample problems to build familiarity. If needed, seek statistics homework help to clarify doubts. By understanding the assignment requirements and preparing accordingly, you set yourself up for success. Before diving into solving the assignment, it is essential to establish a structured approach:
- Understand the Assignment Requirements: Read the assignment carefully and identify the statistical terms, formulas, and computations required.
- Gather Resources: Use textbooks, lecture notes, and online platforms like Statistics Homework Helper to clarify concepts and gather formulas.
- Organize Data: If the assignment involves datasets, structure the data in a table or spreadsheet for easy analysis.
- Use Statistical Software: Tools like Excel, SPSS, or Python can streamline calculations and visualizations.
- Plan Your Work: Divide the assignment into manageable sections, ensuring each term and formula is adequately addressed.
Key Statistical Concepts and Guidelines
Key statistical concepts such as variance, standard deviation, and correlation play a significant role in many assignments. These terms are foundational in analyzing and interpreting data. For instance, understanding the calculation and significance of variance and standard deviation allows you to measure data variability, while concepts like correlation help you understand relationships between variables. When solving assignments, always refer back to these basic concepts, ensuring you apply the correct formula and interpretation. Developing a solid grasp of these guidelines is essential for accuracy in statistical analysis. Below, we integrate the essential statistical terms and their applications into a cohesive framework for solving assignments.
Descriptive Statistics: Understanding and Analyzing Data
Descriptive statistics provide a foundation for summarizing and interpreting data. Key concepts include:
- Range: The difference between the maximum and minimum values in a dataset.
- Variance: Measures the spread of data around the mean.
- Standard Deviation: The square root of variance, representing data dispersion.
- Sum of Squares (SS): The total squared deviation from the mean.
Formula: Range = Max Value − Min Value
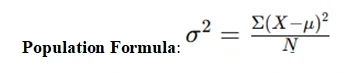
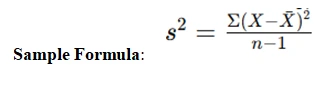




Probability Distributions and Scores
Probability distributions describe how probabilities are assigned to different outcomes. Common types include the normal distribution and the binomial distribution. Understanding these distributions is essential when solving assignments involving hypothesis testing or calculating probabilities. Additionally, statistical scores like Z-scores allow you to standardize data and compare results across different data sets. In assignments, it's important to recognize when to use these distributions and scores, ensuring accurate calculations and interpretations. Mastery of these concepts will aid in more complex problem-solving scenarios. Understanding probability distributions and scores is critical for interpreting statistical relationships.
- Normal Curve: A symmetric, bell-shaped curve representing the distribution of data.
- Z-Score: Represents the number of standard deviations a data point is from the mean.
- Standard Normal Curve: A normal curve where μ=0 and σ=1
- Standard Score: A normalized score based on the standard deviation.
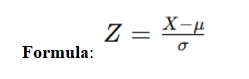
Correlation and Relationships
Correlation analysis is crucial for understanding how two or more variables relate to each other. The correlation coefficient quantifies the strength and direction of a relationship between variables. In statistics assignments, you may be asked to interpret scatterplots and compute correlation coefficients. A positive correlation indicates that variables move in the same direction, while a negative correlation shows an inverse relationship. Understanding these relationships is key for assignments that require the analysis of data trends and patterns. Being able to explain the relationship between variables helps in providing clear, accurate solutions. Assignments often explore relationships between variables using correlation and regression.
- Positive Relationship: Both variables increase together.
- Negative Relationship: One variable increases while the other decreases.
- Scatterplot: A graph displaying the relationship between two variables.
- Correlation Coefficient: Measures the strength and direction of a relationship.
- Regression Toward the Mean: The tendency for extreme scores to move closer to the mean in subsequent measurements.
Pearson Correlation Coefficient Formula:
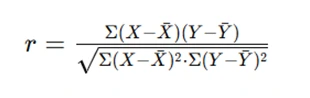
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is used to model the relationship between dependent and independent variables. In statistics assignments, the least squares regression equation helps predict outcomes based on this relationship. Understanding how to compute and interpret regression equations is essential for assignments that involve forecasting or analyzing data trends. Additionally, multiple regression allows for the analysis of more than one predictor variable. It’s important to understand the assumptions of regression models and how to interpret the results accurately to provide insightful analysis and conclusions in your assignments. Regression analysis predicts the value of a dependent variable based on independent variables.
- Least Squares Regression Equation:
- Multiple Regression Equation:
- Standard Error of Estimate: Measures the accuracy of predictions.
Y = a+bX, where b is the slope and a is the intercept.
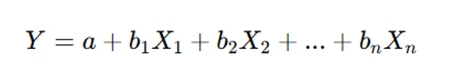
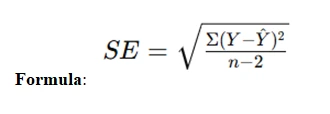
Problem-Solving Techniques
Effective problem-solving in statistics involves a combination of logical thinking and the application of statistical methods. Start by reading the assignment thoroughly, identifying the key variables, and selecting the right statistical techniques to analyze the data. Break the problem into smaller, manageable steps and ensure you apply the correct formulas at each stage. For more complex problems, review past examples or seek statistics homework help. Practicing these techniques regularly will improve your problem-solving skills, making it easier to approach future assignments with confidence. Here are general guidelines to solve problems involving statistical terms and computations:
- Define the Problem: Identify the dataset and the required statistical measures.
- Select Appropriate Formulas: Use the definitions and formulas provided for each concept.
- Perform Calculations Step-by-Step: Clearly show your work to avoid errors.
- Interpret Results: Explain the implications of the results in context.
- Visualize Data: Use graphs like scatterplots or histograms to support findings.
Examples of Statistical Formulas
Understanding and applying statistical formulas is a fundamental part of solving assignments. Examples of these formulas include the variance formula (s² = Σ(xi - x̄)² / (n - 1)) and the Pearson correlation coefficient formula (r = Σ(xi - x̄)(yi - ȳ) / √Σ(xi - x̄)²Σ(yi - ȳ)²). These formulas allow you to quantify data variability, relationships, and trends. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the key formulas related to your assignment and understand when and how to use them correctly. Mastery of these formulas will greatly enhance your ability to solve statistics problems. Assignments may include the following additional computations:
- Sum of Products (SP):
- Variance for Population:
- Variance for Sample:
- Addition Rule for Probability:
- Multiplication Rule for Probability:
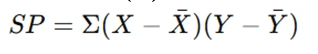
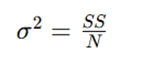
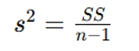
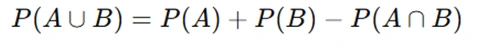
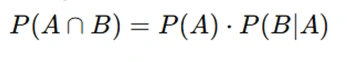
Conclusion
In conclusion, solving statistics assignments requires both a solid understanding of fundamental concepts and the ability to apply formulas accurately. By breaking down the assignment, focusing on key concepts like variance, correlation, and regression, and using problem-solving techniques effectively, you can approach even complex statistical assignments with confidence. Practice and preparation are key to mastering these assignments, and seeking statistics homework help when necessary can provide additional guidance and clarity. Ultimately, developing strong problem-solving skills and a deep understanding of statistical principles will ensure success in your assignments and enhance your academic performance.
.png)








