One-Way ANOVA
| ANOVA | |||||
| Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Reading Before | |||||
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| Between Groups | 2341.061 | 2 | 1170.530 | 3.426 | .036 |
| Within Groups | 42360.337 | 124 | 341.616 | ||
| Total | 44701.397 | 126 | |||
Interpretations: “A one-way between subjects ANOVA was conducted to compare the difference in the Pre-SAT reading scores among different races. There was a statistical significant difference in the Pre-SAT reading scores of the three different race with (F=3.426, p=0.036).
C. t tests - Means: Difference between two independent means (two groups)
Analysis: A priori: Compute required sample size
Input: Tail(s) = Two
Effect size d = 0.5
α err prob = 0.05
Power (1-β err prob) = 0.80
Allocation ratio N2/N1 = 1
Output: Noncentrality parameter δ = 2.8284271
Critical t = 1.9789706
Df = 126
Sample size group 1 = 64
Sample size group 2 = 64
Total sample size = 128
Actual power = 0.8014596
Using G-power analysis the required sample size is 64 for group 1 and 64 for group 2 which will amount to 128 total sample size.
Two-Way ANOVA
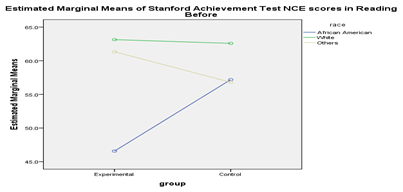
A. Two- Way ANOVA is the appropriate statistical level to use. The two-way ANOVA is used to estimate how the mean of a quantitative variable changes according to the levels of two categorical variables. In this question both race and group are the categorical variables while the Pre-SAT reading scores is the dependent variable.
B.
a. R Squared = .080 (Adjusted R Squared = .042)
| Tests of Between-Subjects Effects | |||||
| Dependent Variable: Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Reading Before | |||||
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
| Corrected Model | 3596.055a | 5 | 719.211 | 2.117 | .068 |
| Intercept | 333707.428 | 1 | 333707.428 | 982.320 | .000 |
| group | 84.123 | 1 | 84.123 | .248 | .620 |
| race | 2976.851 | 2 | 1488.425 | 4.381 | .015 |
| group * race | 1064.266 | 2 | 532.133 | 1.566 | .213 |
| Error | 41105.342 | 121 | 339.714 | ||
| Total | 486021.730 | 127 | |||
| Corrected Total | 44701.397 | 126 | |||
| Multiple Comparisons | ||||||
| Dependent Variable: Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Reading Before Tukey HSD | ||||||
| (I) race | (J) race | Mean Difference (I-J) | Std. Error | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| African American | White | -9.505* | 3.6212 | .026 | -18.098 | -.913 |
| Others | -5.740 | 4.9706 | .482 | -17.535 | 6.054 | |
| White | African American | 9.505* | 3.6212 | .026 | .913 | 18.098 |
| Others | 3.765 | 4.7305 | .706 | -7.460 | 14.990 | |
| Others | African American | 5.740 | 4.9706 | .482 | -6.054 | 17.535 |
| White | -3.765 | 4.7305 | .706 | -14.990 | 7.460 | |
| Correlations | ||||
| Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Reading After | Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Language After | Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Math After | ||
| Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Reading After | Pearson Correlation | 1 | .737** | .789** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | .000 | ||
| N | 148 | 148 | 148 | |
| Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Language After | Pearson Correlation | .737** | 1 | .738** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | .000 | ||
| N | 148 | 148 | 148 | |
| Stanford Achievement Test NCE scores in Math After | Pearson Correlation | .789** | .738** | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | .000 | .000 | ||
| N | 148 | 148 | 148 | |